forward
class Module(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Module, self).__init__()
# ......
def forward(self, x):
# ......
return x
data = ..... #输入数据
# 实例化一个对象
module = Module()
# 前向传播
module(data)
# 而不是使用下面的
# module.forward(data) 因为 python calss 中的call和init方法.使得module(data)等价与module.forward(data)
#50000张训练图片
train_set = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True,
download=False, transform=transform)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=36,
shuffle=False, num_workers=0)数据集通过torchvision.dataset.进行设置下载,通过一个dataloader使其成为训练中可用的参数
outputs = net(val_image) # [batch, 10]
predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
accuracy = (predict_y == val_label).sum().item() / val_label.size(0)outputs为500010,第0维为图片序号,第一维为10个类别的数值,最大的一般视为识别的类
*torch.max(input, dim, keepdim=False, out=None)**
Returns a namedtuple (values, indices) where values is the maximum value of each row of the input tensor in the given dimension dim. And indices is the index location of each maximum value found (argmax).所以predict_y为最大值的索引
predict_y == val_label为5000个true或false组成的tensor列表用sum将它们合成一个tensor数,然后.item变为数
torch.norm(input, p, dim, out=None,keepdim=False)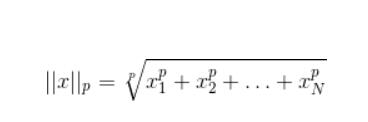
input (Tensor) – 输入张量
p (float) – 范数计算中的幂指数值
dim (int) – 缩减的维度
out (Tensor, optional) – 结果张量
keepdim(bool)– 保持输出的维度
torch.tensor(X).type(torch.FloatTensor)
将列表或nparray转为tensor变量,数据类型为torch.FloatTensor
Variable(tensor)
将tensor变成tensor变量,用于梯度计算
点乘
res=x.mul(y) 如何将数据文件中的参数赋值给我们的网络?
首先网络实例化后
nn=NN()调试输出nn.state_dict()可以打印结构参数
OrderedDict([('in_layer.weight',
tensor([[-1.0562e-08, 2.1941e-09, -6.9222e-06, ..., -1.3053e-05,
-5.0418e-06, 2.8046e-09],
[ 7.6617e-09, -9.7587e-09, 1.0474e-06, ..., -5.6013e-05,
2.0094e-07, 3.5442e-09],
[-8.7765e-09, 8.1604e-09, -1.4774e-06, ..., -1.2095e-04,
-2.3367e-06, -7.5067e-09],
...,
[-8.8927e-09, -9.8197e-09, -7.7838e-06, ..., 2.3531e-05,
-3.2548e-06, 9.0250e-09],
[ 3.0518e-10, 2.5606e-09, -2.1194e-06, ..., -8.6176e-04,
9.4345e-05, 3.8376e-09],
[ 8.8588e-09, -6.5752e-10, -8.8164e-06, ..., -1.8037e-06,
-8.1446e-06, 8.7945e-09]])),
('in_layer.bias',
tensor([-0.0226, -0.0984, 0.1162, -0.2397, -0.7316, -0.5979, 0.1546, -0.0337,
-0.4107, 0.0235, 0.2477, 0.2653, 0.0943, 0.2022, -0.2030, 0.1046,
0.1489, -0.0379, -0.3320, -0.2977, -0.4842, -0.3898, -0.1832, -0.7021,
-0.3509])),
('hd_layer.weight',
tensor([[-1.2124, -0.1019, -2.3685, -1.0578, -2.2082, 0.5638, 1.2111, 2.2103,
0.4446, -1.1824, 1.0429, -1.6056, 1.3042, 1.3718, 1.7483, -0.2337,
-1.5201, 1.1532, 0.1037, -0.3721, -0.6153, -0.1257, -2.2719, -0.7184,
-1.2969],
[ 0.6156, -1.2655, 1.8575, -0.9185, -0.0550, -0.3859, 1.2952, -1.5684,
-0.9703, -2.1833, -2.8503, -2.0773, 1.6316, 0.3490, 1.8279, -2.4417,
-0.8563, -0.2983, -2.0795, -1.2933, 0.8998, 0.2831, 2.3118, -2.4644,
1.4566],
...,
[-1.4394, -1.2181, 0.7109, 0.4522, -0.3595, 0.6228, -0.6701, -0.7069,
0.0631, -1.2320, -1.7465, -2.7196, -2.2144, -1.6931, -0.9093, 0.8785,
1.1866, -1.8704, 0.3980, 1.7211, -1.3693, 0.8581, -0.2478, 1.2801,
-1.3275]])),
('hd_layer.bias',
tensor([-0.7610, -0.6179, -0.6893, -0.6783, -0.5966, -0.8779, -0.5275, -0.7490,
-0.6665, -0.4609]))])再用字典将我们预设的参数按key值写好,再读取即可
dict={}
dict['in_layer.weight'] = torch.tensor(ex3weights['Theta1'][:,1:]).type(torch.FloatTensor)
dict['in_layer.bias'] = torch.tensor(ex3weights['Theta1'][:, 0]).type(torch.FloatTensor)
dict['hd_layer.weight'] = torch.tensor(ex3weights['Theta2'][:, 1:]).type(torch.FloatTensor)
dict['hd_layer.bias'] = torch.tensor(ex3weights['Theta2'][:, 0]).type(torch.FloatTensor)
nn.load_state_dict(dict) ##如何自定义loss
使用nn.module
class my_loss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self,out,y_data,module=None,lamda=0):
h1=-1*y_data.mul(torch.log(out))
h2=-1*(1-y_data).mul(torch.log(1-out))
J=h1.sum()+h2.sum()
regul=lamda/2/y_data.shape[0]*(torch.sum(module.in_layer.weight**2)+torch.sum(module.hd_layer.weight**2))
return J/y_data.shape[0]+regul本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 3.0协议 。转载请注明出处!